Dust explosion is a phenomenon that explosion occurs due to the presence of an ignition source with combustible dust cloud in the air.
Combustible dust could explode in the presence of a certain ignition source if forming a dust cloud in the air with a certain concentration. The following tests are conducted to the dust from viewpoints of "likelihood of explosion" and "explosion severity". The explosivity of the dust ,however, depends considerably on the kind and particle size of the dust, and test results change depending on the apparatus and method as gas explosion test results. Therefore, obtained data need to be analyzed carefully. In 2002, JIS Z 8817 "Test method for explosion pressure and rate of pressure rise of combustible dusts" and JIS Z 8818 "Test method for minimum explosive concentration of combustible dusts" were issued. Since June 2003, SCAS has adopted a test method in compliance with the JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) to measure the lower explosion limit , explosion pressure, rate of pressure rise, and explosion indices (Kmax).
Test Items
- Lower explosion limit (Minimum explosive concentration)
- Limiting oxygen concentration
- Explosion pressure and Rate of pressure rise
- Minimum ignition energy
Commentary
| apparatus | temperature | initial pressure | energy measurement range | sample container | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lower explosion limit of concentration | tube type (conforming to JIS Z8818) | room temperature | atmospheric pressure | - | - |
| limiting oxygen concentration | tube type | room temperature | atmospheric pressure | - | - |
| explosion pressure and pressure rate of rise | 20 L, sphere type (conforming to JIS Z8817) |
room temperature | atmospheric pressure | - | - |
| minimum ignition energy (minimum combustion energy) | tube type | room temperature | atmospheric pressure | several mJ to about 1,000 mJ | - |
Lower explosion limit (Minimum explosive concentration)
One of the properties for dust explosion is the dust concentration of a dust/air mixture. Dust explosion could occur when the concentration is in a certain range. The lower limit of the concentration range is called lower explosion limit, which indicates likelihood of the dust explosion. Since the lower explosion limit depends on particle diameter, the diameter needs to be determined in advance. Target of test is a dust cloud, for this reason the lower explosion limit is usually measured for particles passing through a sieve of a 63 μm mesh. Contact us if you need measurement as it is for some reason.
Limiting oxygen concentration
If the oxygen concentration of a dust/air mixture is decreased to a certain lower limit by addition of nitrogen or other inert gases, dust explosion could be prevented. This lower limit of the oxygen concentration is called limiting oxygen concentration. SCAS can measure the limiting oxygen concentration of a mixture of dust, oxygen, and nitrogen (or other inert gases). Since the limiting oxygen concentration changes depending on the particle diameter of the dust, the diameter needs to be determined in advance. Usually the limiting oxygen concentration is measured for particles passing through a sieve of a 63 μm mesh.
Explosion pressure and Rate of pressure rise
The pressure of enclosed space increases if a dust/air mixture explodes in the confined space. The explosion pressure reaches the maximum value at an optimal dust concentration, which is called maximum explosion pressure of the dust/air mixture. The maximum slope of the explosion pressure vs time curve is called maximum rate of pressure rise. The explosion pressure depends on the kind of the dust, particle diameter, concentration of the dust, vessel shape, and turbulence. Therefore, a test using 20 L or larger explosion test apparatus is necessary to obtain the explosion indices (Kmax). SCAS uses 20 L sphere explosion apparatus for the measurement. Usually these properties are measured for particles passing through a sieve of a 63 μm mesh.
Minimum ignition energy
A dust/air mixture would explode when ignition energy larger than a certain value that depends on the pressure, temperature, and dust concentration. The limiting energy of the ignition is called minimum ignition energy of the dust/air mixture. It is an important index to decide whether the dust can be handled in the air or should be handled in the inert atmosphere. SCAS can measures using tube-type dust explosion test apparatus with capacity spark power supply. Since the minimum ignition energy changes depending on the particle diameter of the dust, the diameter needs to be determined in advance. Usually the minimum ignition energy is measured for particles passing through a sieve of a 63 μm mesh. Contact us if you need a test based on MIKE-3 in conformance with IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) Standard*1.
Note: In 2016, JIS Z 8834 "Method for determining minimum ignition energy of dust/air mixtures" was issued.
*1 IEC 1241-2-3 "Electrical Apparatus for Use in the Presence of Combustible Dust, Part 2: Test Methods, Section 3: Method for Determining Minimum Ignition Energy of Dust/Air Mixtures", 1994
Equipments


Dust Explosion Tests : Evaluation Procedure (a typical example)
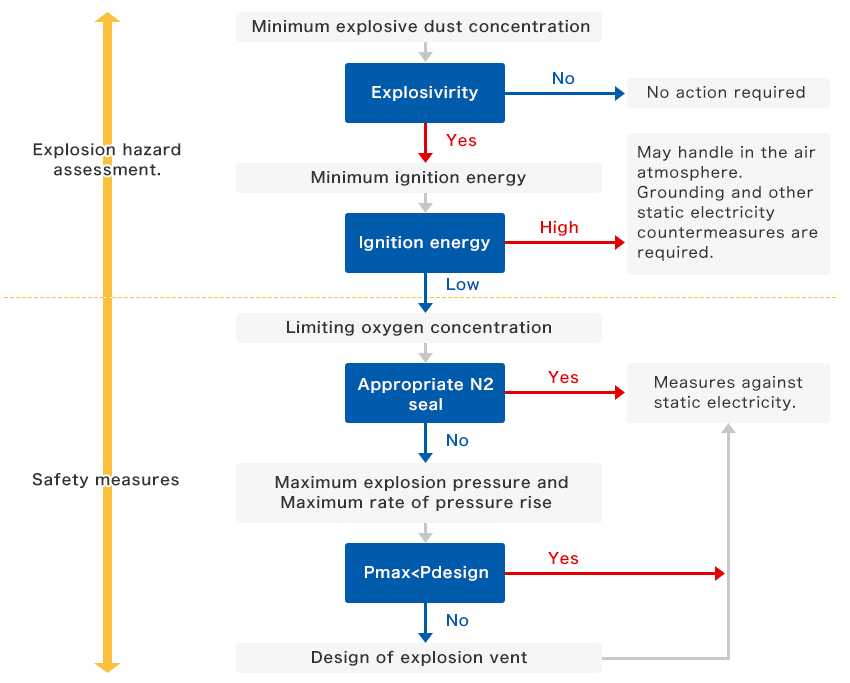 Reference:Supervised by Japan Society for Safety Engineering,”Jissen Anzenkougaku(safety engineering practice) series 1,
Reference:Supervised by Japan Society for Safety Engineering,”Jissen Anzenkougaku(safety engineering practice) series 1,
Technical News
Contact Us for Services
For inquiries and requests concerning services of analysis, measurements, products and consulting, please contact us via inquiry form.
